UK higher education institutions along with Jisc are currently in negotiation for a new “read and publish” agreement (also referred to as “transitional” or “transformative” agreements) with the publisher Springer Nature. Our current agreement runs to the end of December 2022 and we are seeking a new agreement that will not only enable us to read the journals covered by the deal, but also enables researchers to publish open access in those journals at no additional cost.
The sector has agreed criteria for our negotiations. Agreements should
- Reduce and constrain costs
- Provide full and immediate open access publishing
- Aid compliance with funder open access requirements
- Be transparent, fair, and reasonable
- Deliver improvements in service, workflows, and discovery
We achieved these aims with last year’s negotiations with Elsevier and are seeking to do so with Springer Nature. In addition to seeking a renewal of the existing Springer Compact agreement which has been running since 2016, we are also seeking to include Nature research journals and Palgrave journals.
If you are reading this and wondering what a “transitional” agreement is, my colleague David Phillips wrote about these in an earlier blog. At the time David noted that we had 11 such agreements in place at Imperial. This has now risen to 33 with fully covered publishing costs plus further agreements which include discounted article processing charges (APCs). Back in 2019, only 9% of sector spend enabled full OA publishing. That figure is now over 80%.
Why are the negotiations criteria important for researchers?
It is worth taking a moment to reflect on the sector criteria and what they mean for academic authors:
Reduce and constrain costs
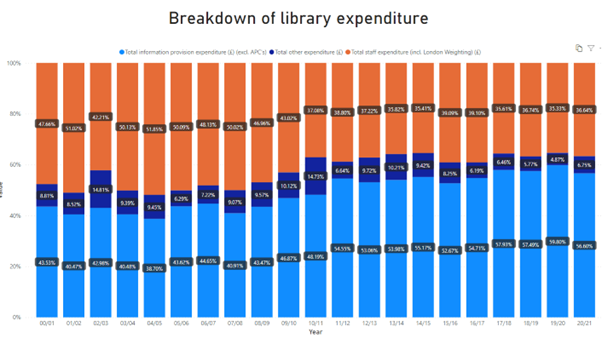
- To be sustainable, the costs of reading and publishing cannot continue rising more than that of inflation. Back at the turn of the century, under 44% of Imperial’s Library Services budget was spent on content. Today it is closer to 60% and further increases are simply not sustainable either for Imperial or for the sector. Our most recent Jisc negotiations went some way to stem the rise and we need the agreement with Springer Nature to similarly deliver. To illustrate the impact of increasing content prices, the chart below shows the breakdown of expenditure on staff, operations, and content costs.
Provide full and immediate open access publishing
- Jisc have a very helpful webpage detailing the benefits of open access publishing and from which this illustration is sourced:
Aid compliance with funder open access requirements
- One of the questions that libraries frequently get asked is what should authors do to both ensure they meet funder obligations, and that their research outputs are eligible for the Research Excellence Framework – the REF. Our agreement with Springer Nature needs to enable both, affordably.
Be transparent, fair, and reasonable
- As researchers you have secured the grant funding, you have assembled the team, drawn up the protocols, undertaken the research, undertaken the analysis and written up the findings. You then undertake the peer review. All of the above without payment from the publisher. You may also act as editors for journals, often on a voluntary basis with no compensation. Libraries then pay the publisher for publishing and content provision services. We need those payments to be transparent, fair and reasonable, reflecting the contribution researchers already make to the system.
Deliver improvements in service, workflows, and discovery
- We are in a transition from paying for content to paying for publishing services on behalf of researchers. It is really important that those services are efficient for all parties otherwise we simply introduce additional administrative costs into the system. For authors, time spent battling a clunky submissions system or an unclear or conflicting publishing contract, especially processes which involve back and forth with libraries, are taking time away from your research activities as well as adding to admin burdens.
- It is of course vital that research is discoverable for it to be built on and to have impact.
What next?
Negotiations
- These are ongoing. I’m closely involved as a member of the UUK/Jisc Content Negotiations Strategy Group, as chair of the Jisc Content Expert Group and as a member of the Springer Nature Negotiations Team. Our next negotiations meeting with the publisher is scheduled for 14th November.
Researchers can continue to publish in SN journals and meet both funder OA obligations and have REF eligibility
- The UKRI Open Access Policy which came into force in April 2022 is accompanied by a FAQ which includes the following statement:
“It is the intention that the UK higher education funding bodies will consider a UKRI open access compliant publication to meet any future national research assessment open access policy without additional action from the author and/or institution”
- To be sure that your research output both meets funder requirements and is eligible for the next REF, we advise that you insert the following Rights Assertion Statement on all submitted articles (not just Springer Nature):
“For the purpose of open access, the author has applied a ‘Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) licence to any Author Accepted Manuscript version arising”
If you have questions or want further information
- See if Imperial’s existing open access webpages and the UKRI Open Access Policy help
- Contact the OA team
- Subscribe to the Imperial Open Research Newsletter
- Invite us along to talk to your research group / department
For other activities during #OAWeek2022 see this post by my colleague John Murtagh.
About me: I am Director of Library Services at Imperial College London. My profile is here and you can find me on twitter @ChrisBanks. I have an ORCiD and you can get yours here


