Coding along with Azure Databricks and MoJ’s Splink

In January, our ICT team supported and took part in a Public Sector Code-Along workshop at Imperial’s White City Advanced Hackspace with 60 other data specialists from across public sector organisations, with representatives from Microsoft, Databricks the Ministry of Justice (MoJ)’s Splink team and the National Innovation Centre for Data (NICD).
This event focussed on the MoJ’s Splink package:
Splink is a PySpark package that allows you to link millions of distinct records that refer to an individual entity but lack a consistent identifier. It applies established statistical comparison methods to detect whether records in a dataset related to the same thing by comparing values in any column, and assessing the probability of a match that would be impossible to do manually across large datasets – for example it can be used to detect if two or more similar records amongst millions are actually related to the same individual person.
Databricks is a unified set of tools for building, deploying, sharing, and maintaining enterprise-grade data solutions at scale. It is the technical solution that we use at Imperial to power the Unified Data Platform, launched by our Data and Analytics product line in 2022.
We also heard from keynote speakers:
- Paul Watson, Director of NICD, who gave an overview of the work they are doing to support the National Data Strategy and the skilling up and knowledge transfer.
- Robert Porteous, Deputy Director of Data Strategy, Implementation and Evidence at DCMS, who spoke about the National Data Strategy work, data standards, data share and data challenges.
The workshop gave us the opportunity to get to grips with a government endorsed external public sector package within Databricks. The code from Splink is available in a Databricks workbook that can be easily imported into our Databricks account.
Improving our data use at the College
The Splink tool has a lot of potential to allow controlled cross-system record matching with many uses. It allows a solid statistical model to be built, trained and then ported between technologies.
“Splink could allow us to develop solid common definitions that would be transparent and auditable. For example, it could help when the College wants to check for things like spotting duplicate people in records (e.g. CID deduping), connecting building data between systems when there are no common building identifiers and so on.”
Andrew Lewis, Information Insight Analyst, ICT.
Working with real word data
Andrew explains what they achieved at the event, “In the workshop we focussed on some real-world data available data sourced from Companies House. The hack involved training a statistical model to create rules for checking data in columns such as first name, date-of-birth, postcode etc and using accepted stats methods of scoring closeness of matches.
This chart below shows examples of how the models can be trained to acceptable levels. (Image from Splink tutorials available with code.)
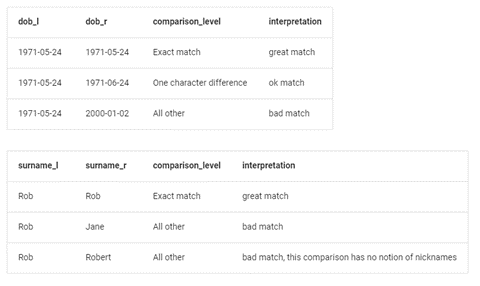
Andrew suggests “It’s too detailed a subject to cover in this post, but Splink has really powerful and robust settings that allow comparisons to be made much faster than other solutions, and with as fine or coarse levels of details as we could need in the rules. It is possible to separate exact matches from probable matches and define what we accept as “must be 100%”, “good enough”, “close – check these” or whatever.”
This chart below shows how applying the probability rules in sequence can greatly increase the chances of spotting data matches, in a way that is automatable and auditable to a defined statistical tolerance. (Image from Splink tutorials available with code.)
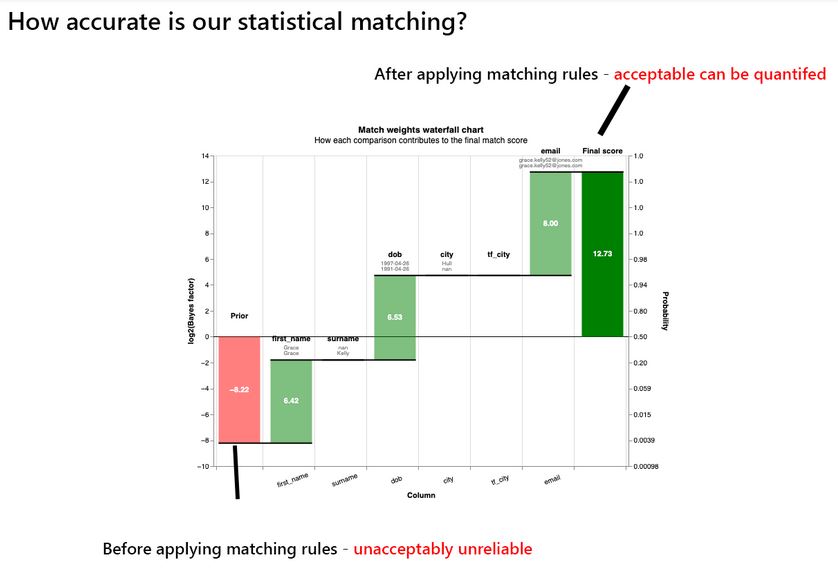
Summary
Overall, this was a great day. We made contact with lots of data practitioners in other public sector organisations and learned about the potential of Splink.
When our analysts and data professionals spend huge amounts of time retrieving, merging, cleaning and verifying College data, it’s time not spent doing the valuable work of understanding and synthesising their analysis into actionable information. Splink has the potential to do this automatically at scale faster than other tools available.

If you want to find out more about how we are using Databricks at the College you can contact our colleagues:
- Richard Howells, Head of Technology Office
- Andrew Lewis, Information Insight Analyst
- Jose Maria Vidal Fidel, Product Developer
- Maria Teresa Douglas, Data and Analytics Product Owner
- Henry Nwiido, Data Domain Specialist
- Nelson Cerqueira, Solutions Architect
- Cho Fung Chan, Data Specialist
- James Clubbe, Data Engineer (Data Specialist)
- Irene Kalkanis, Data and Innovation Lead