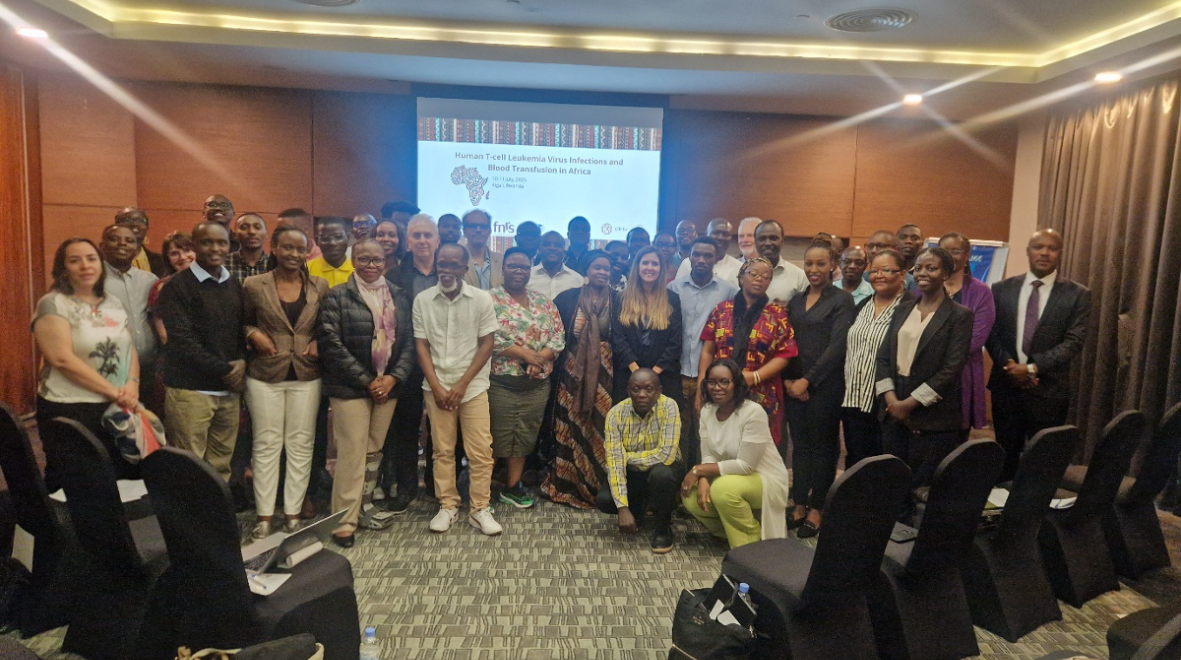

HTLV-1 is a little known but serious virus that can cause life-threatening illnesses, including blood cancer and neurological disease. In many African countries, there is still a lack of research and policies to address it. Dr Carolina Rosadas, Research Fellow in Imperial’s Department of Infectious Disease, writes about bringing together scientists, health officials, policymakers, and community representatives from 18 countries for a groundbreaking workshop in Rwanda – sparking new collaborations, research networks, and strategies to combat this overlooked infection.
Based in the Department of Infectious Disease, I am a Research Fellow focusing on HTLV-1 – an understudied infection that disproportionately impacts underserved communities, particularly in Africa. HTLV-1 can cause severe and often fatal conditions, including blood cancer and neurological disease. There is no treatment for this life-long infection, but prevention is possible.
Despite recent global advances and the formal recognition of HTLV as a priority by the World Health Organization (WHO), many countries in Africa still lack sufficient data and policies to address it. My project aimed to promote local research and help translate knowledge into policy by encouraging multidisciplinary and multi-stakeholder engagement.


 October is Breast Cancer Awareness Month. This is a crucial time to raise awareness about screening, treatment, and prevention of breast cancer. PhD student, Sophia D’Alessandro from the
October is Breast Cancer Awareness Month. This is a crucial time to raise awareness about screening, treatment, and prevention of breast cancer. PhD student, Sophia D’Alessandro from the 


 Kelly Gleason introduces a guide,
Kelly Gleason introduces a guide,