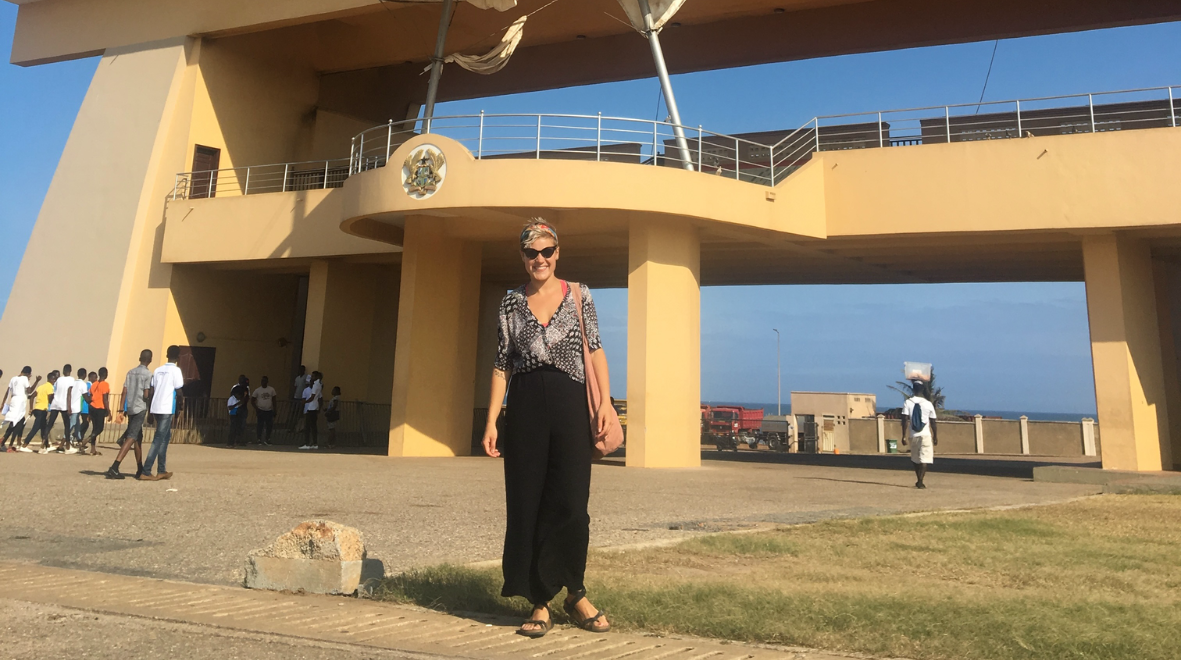

LGBTQIA+ scientists can face nuanced challenges when travelling abroad to conduct research. Bethan Cracknell Daniels, Research Postgraduate in the School of Public Health, reflects on her time in Ghana supporting infectious disease control, and how the LGBTQIA+ International Support Group are advocating for a more inclusive global scientific community.
While applying for my PhD in Infectious Disease Modelling at Imperial in 2019, I wanted to gain hands-on experience in infectious disease control. At the time, I was an undergraduate student studying Immunology at the University of Manchester. I applied for an internship with a laboratory on the edge of Accra, Ghana, providing infectious disease diagnosis to a local hospital. I was excited to be accepted and immediately went about booking flights and organising my visa.
It was only a week before my flight that I learned Ghana criminalises homosexuality, with physical homophobic attacks against LGBTQIA+ individuals being common. As a queer woman with a same-sex partner, I was nervous. Living in Manchester, with its famous gay village, I was very open about my sexuality and thought nothing of walking down the street holding hands with my girlfriend. Unsure of how to navigate being gay in Ghana, I eventually decided to tell people I didn’t have a partner, effectively returning myself to the closet.





 Kelly Gleason introduces a guide,
Kelly Gleason introduces a guide,