This festive period, Three Wise Women from the Faculty of Medicine give us the gift of wisdom.
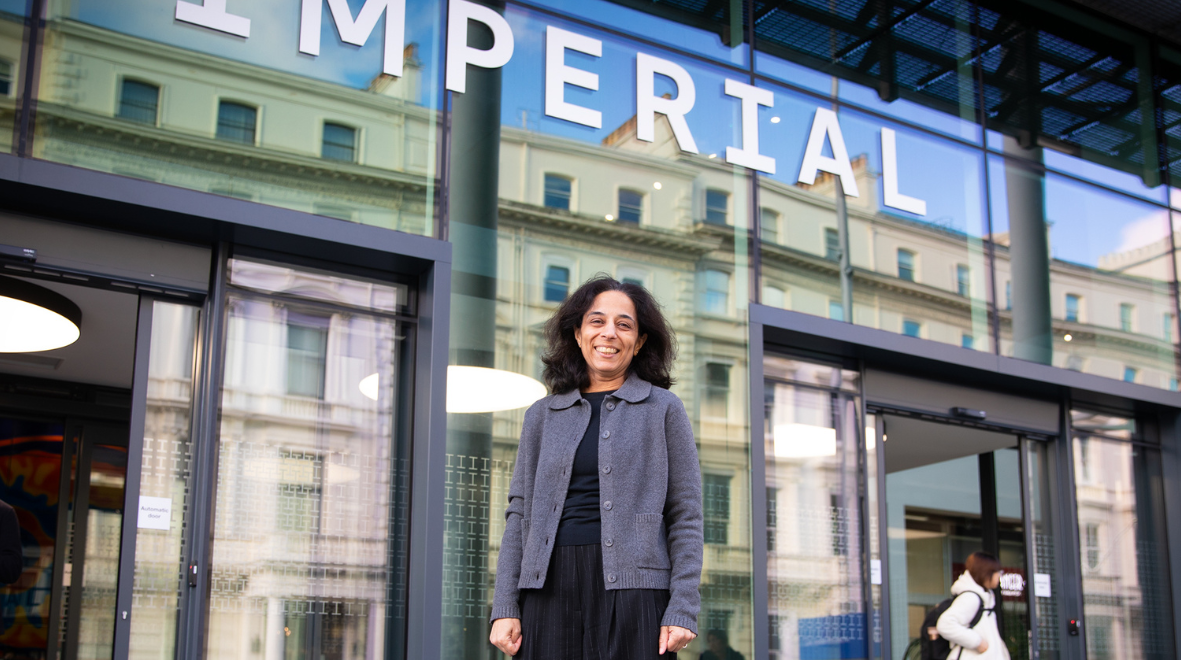
Professor Sejal Saglani, Professor of Paediatric Respiratory Medicine in the National Heart and Lung Institute and Director of Imperial’s Centre for Paediatrics and Child Health (PaeCH), shines a light on the pressing need to transform how we understand and manage childhood asthma. She discusses why the youngest children face the greatest challenges, how early-life illness shapes long-term health, and the critical role of research and advocacy in addressing inequalities that begin from birth. Her blog is a call to action: if we are to secure lifelong health, we must begin with the earliest years.
Asthma is the most common long-term condition affecting children of all ages worldwide. In the UK, around 10% of children live with asthma – meaning at least two or three children in every classroom. Among these, those under the age of five face the greatest challenges: they experience the most acute attacks, have the highest number of hospital admissions, and account for 75% of all emergency department visits for childhood asthma. Despite this significant burden, the rate of attacks and hospitalisations have remained unchanged for over 20 years.
This time of year brings the issue into sharp focus. Most admissions occur during the autumn and winter months. Parents and families live in a constant state of vigilance, never knowing whether the next runny nose will simply be a cold or will escalate into yet another visit to hospital with wheezing and breathlessness.

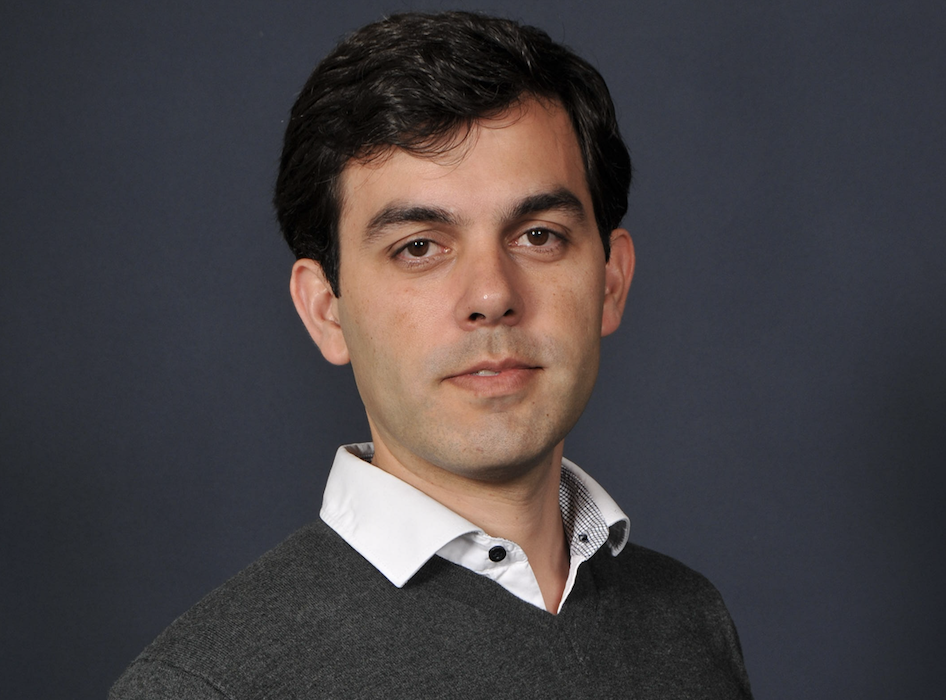
 Dr Amit Kaura,
Dr Amit Kaura, 
 The path to a smokefree generation demands decisive action and innovative strategies. To mark World No Tobacco Day,
The path to a smokefree generation demands decisive action and innovative strategies. To mark World No Tobacco Day,  To mark Women at Imperial Week, we’re spotlighting Fama Manneh, a 2nd-year PhD student, from the
To mark Women at Imperial Week, we’re spotlighting Fama Manneh, a 2nd-year PhD student, from the  Born on what would eventually be recognized as World AIDS Day in the 1970s, Dr Mike Emerson, now affiliated with the National Heart and Lung Institute, relocated to vibrant London during the early 1990s amidst the fervour of the Britpop era. In the backdrop of Blur and Pulp melodies, 1990s London faced the AIDS crisis. Three decades later, he is at the helm of a team investigating cardiovascular ailments in people with HIV. In this piece, Dr Emerson reflects on the advancements in HIV diagnosis and therapy, and reiterates the ongoing importance of National HIV Testing Week.
Born on what would eventually be recognized as World AIDS Day in the 1970s, Dr Mike Emerson, now affiliated with the National Heart and Lung Institute, relocated to vibrant London during the early 1990s amidst the fervour of the Britpop era. In the backdrop of Blur and Pulp melodies, 1990s London faced the AIDS crisis. Three decades later, he is at the helm of a team investigating cardiovascular ailments in people with HIV. In this piece, Dr Emerson reflects on the advancements in HIV diagnosis and therapy, and reiterates the ongoing importance of National HIV Testing Week.