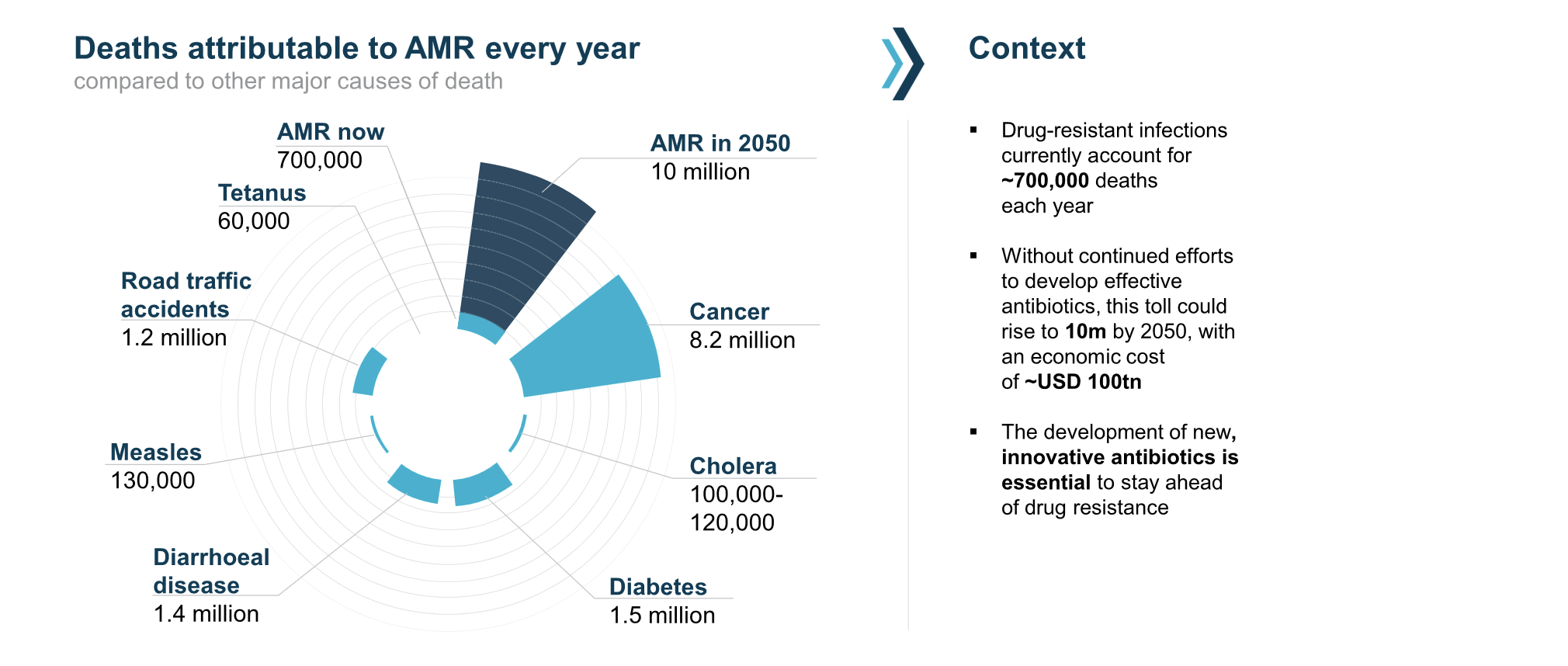
Diabetes now affects over half a billion people globally, including 3.8 million people in England. Type 2 diabetes, which accounts for 90-95% of all cases, has obesity as its primary modifiable risk factor. Expanding waistlines, both nationally and globally, have driven a steady increase in type 2 diabetes rates in recent decades. To mark World Diabetes Day, Professor Jonathan Valabhji OBE, from the Department of Metabolism, Digestion and Reproduction, reflects on his 30 years of experience in the field, in clinical practice, in national leadership, and in clinical and epidemiological research.
My background in Diabetes research and clinical practice
I qualified as a doctor in 1990 from St Bartholomew’s Hospital Medical College, London. I undertook specialist training in diabetes, endocrinology, and general medicine in North-West London, and landed at Imperial College in 1997 to undertake my MD (Doctor of Medicine degree) as a British Heart Foundation Junior Research Fellow. In those early years, I was interested in cardiovascular disease in diabetes, which at that point was responsible for the majority of deaths in people with diabetes. My work centred on understanding the paradox in type 1 diabetes: although patients often displayed healthy cholesterol profiles, they were at elevated risk of heart attacks and strokes. I spent 3 years in a lipid laboratory, using ultracentrifugation (a technique used to separate and isolate particles based on their density) to isolate high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol particles from blood samples, to try to disentangle the paradox.
Population-level progress in cardiovascular health
While I like to think that some of that early research advanced the field a little, it was other epidemiological and societal factors that saw cardiovascular disease fall in people with diabetes over the next two decades. Public health initiatives, such as reduced smoking rates, and improved management of blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol, have collectively driven a marked decrease in cardiovascular complications, resulting in longer lifespans for people with diabetes. However, with this success came new challenges, as other and multiple long-term conditions (MLTCs) have increasingly become leading causes of illness and death. This has complicated care for patients, healthcare professionals, and the NHS. At the same time, obesity has driven younger onset of type 2 diabetes, contributing to accelerated development of MLTCs at younger ages.
 Virus Appreciation Day, celebrated annually on 3 October, serves a dual purpose: to foster respect and understanding for viruses while raising awareness about their serious impacts on health. To mark the day,
Virus Appreciation Day, celebrated annually on 3 October, serves a dual purpose: to foster respect and understanding for viruses while raising awareness about their serious impacts on health. To mark the day, 
 The path to a smokefree generation demands decisive action and innovative strategies. To mark World No Tobacco Day,
The path to a smokefree generation demands decisive action and innovative strategies. To mark World No Tobacco Day,  Born on what would eventually be recognized as World AIDS Day in the 1970s, Dr Mike Emerson, now affiliated with the National Heart and Lung Institute, relocated to vibrant London during the early 1990s amidst the fervour of the Britpop era. In the backdrop of Blur and Pulp melodies, 1990s London faced the AIDS crisis. Three decades later, he is at the helm of a team investigating cardiovascular ailments in people with HIV. In this piece, Dr Emerson reflects on the advancements in HIV diagnosis and therapy, and reiterates the ongoing importance of National HIV Testing Week.
Born on what would eventually be recognized as World AIDS Day in the 1970s, Dr Mike Emerson, now affiliated with the National Heart and Lung Institute, relocated to vibrant London during the early 1990s amidst the fervour of the Britpop era. In the backdrop of Blur and Pulp melodies, 1990s London faced the AIDS crisis. Three decades later, he is at the helm of a team investigating cardiovascular ailments in people with HIV. In this piece, Dr Emerson reflects on the advancements in HIV diagnosis and therapy, and reiterates the ongoing importance of National HIV Testing Week.