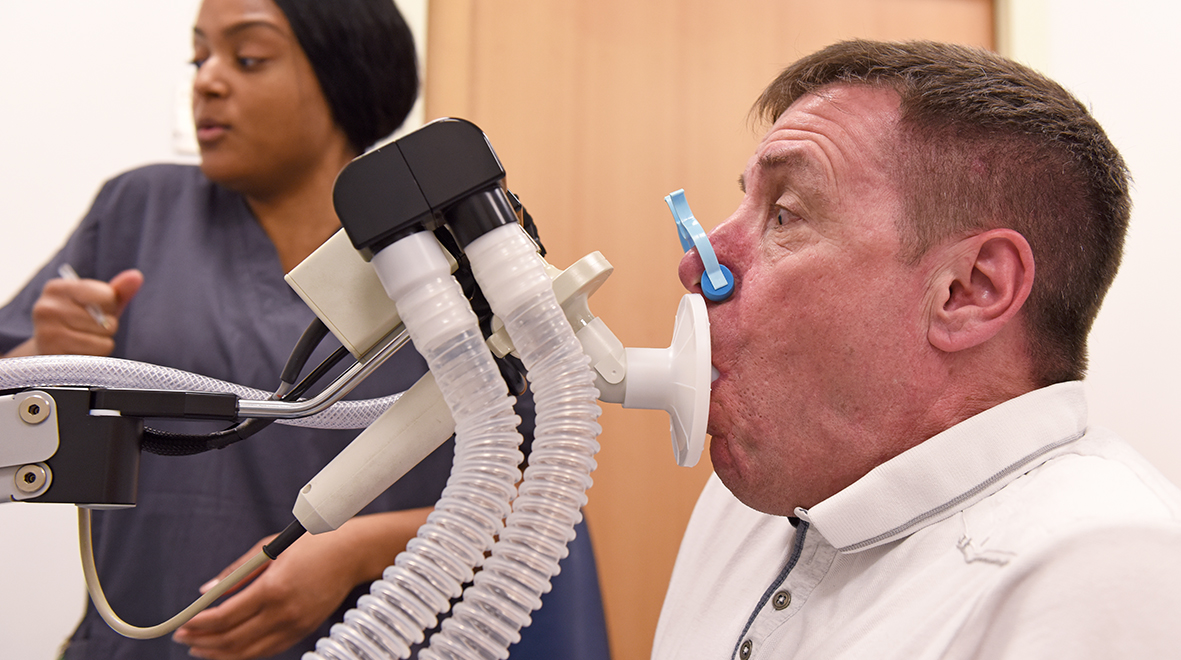
COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, has traditionally been thought of as an irreversible and somewhat hopeless condition. Many patients with COPD may be missing out on the possibility for a dramatic improvement in their condition. They deserve better.
COPD, is a common and important condition. There are 1.3 million people with a diagnosis of COPD in the UK and it’s now the third leading cause of death worldwide. The main symptoms are breathlessness, cough and sputum production.
The term COPD encompasses a range of pathological processes, usually caused by smoking or inhaling other noxious materials. It includes chronic bronchitis – inflammation and damage to airways as well as emphysema – destruction of the lung tissue itself and damage to the blood vessels in the lung. In emphysema the walls of the alveoli (air sacs) break down. The lung tissue loses its elasticity and becomes baggy, and air gets trapped in the lungs making breathing uncomfortable. In some people the condition is caused by alpha one antitrypsin (A1AT) deficiency; the inherited lack of a defensive enzyme, which makes their lungs much more vulnerable. (more…)
Read Lung volume reduction – new hopes and missed opportunities in COPD in full



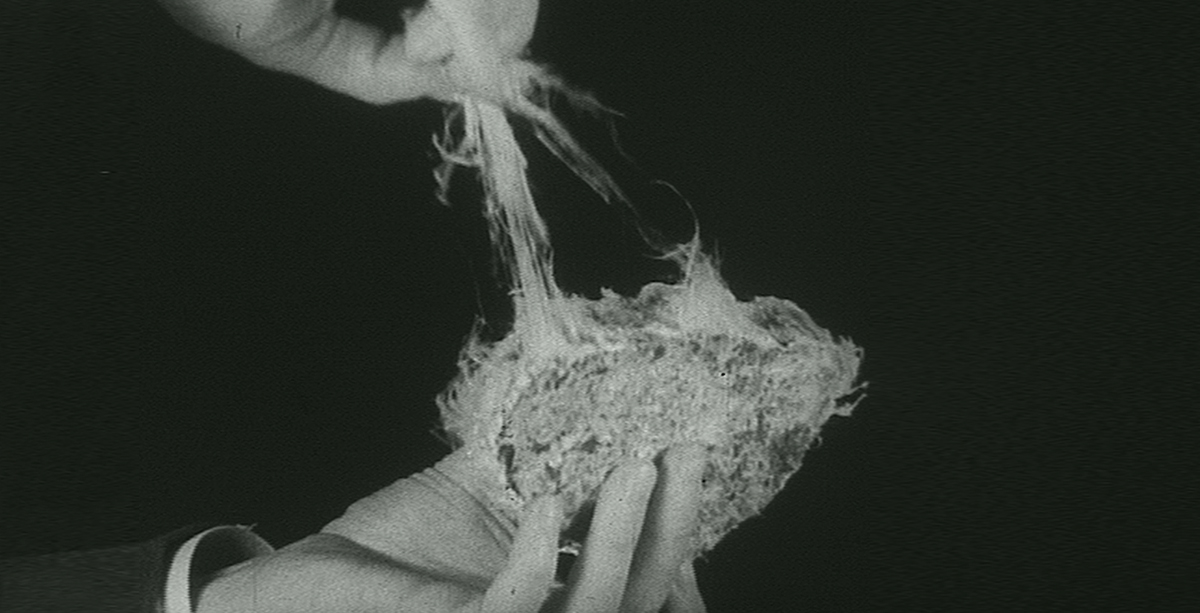 An eye-opening account by Professor Sir Tony Newman Taylor on how asbestos has gone from ‘magic mineral’ to deadly dust that can cause mesothelioma.
An eye-opening account by Professor Sir Tony Newman Taylor on how asbestos has gone from ‘magic mineral’ to deadly dust that can cause mesothelioma.

 James Moss, a Teaching Fellow, provides an insight into his role, from exam marking to supporting research projects.
James Moss, a Teaching Fellow, provides an insight into his role, from exam marking to supporting research projects. 
